Python break and continue statement
In this tutorial, you will learn about Python break and continue statement. Python break statement is used to jump out of the loop and continue statement is used to continue iterating the loop by skipping some part of codes.
| Break and continue: Introduction |
| Python break statement |
| Python continue statement |

Python programming break and continue statement
Until now we have learned about looping in which we repeatedly execute a block of code till the specified condition is met.
What if we wanted to jump out of the loop or continue the loop by skipping some code without checking the test expression in the loop?
For this, there is Python break and continue statement. With break statement we can jump out of the loop without further checking the test expression of the loop and with continue statement, we can continue looping by skipping some part of the code.
Python break statement
The break statement is used to jump out of the loop by skipping the remaining code without further testing the test expression of that loop. Basically, it is used to terminate while loop or for loop in Python.
It interrupts the flow of the program by breaking the loop and continues the execution of code which is outside the loop.
Syntax of Python break statement
while (test_expression1):
statement(s)
if (test_expression2):
break
|
for var in sequence:
statement(s)
if (test_expression2):
break
|
Flowchart of Python break statement

How break statement works in python?

Example of Python break statement in while loop
In the following example, while loop is set to print the first 8 items in the tuple. But what actually happens is, when the count is equal to 4, it triggers if statement and the break statement inside it is invoked making the flow of program jump out of the loop.
[adsense1]
#declaring a tuple
num = (1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8)
count = 0
while (count<9):
print (num[count])
count = count+1
if count == 4:
break
print ('End of program')
Output
This script will generate following output.
1 2 3 4 End of program
Example of Python break statement in for loop
Following example will do the same exact thing as above program but using a for loop.
#declaring a tuple
num = (1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8)
count = 0
for item in num:
print (item)
count = count+1
if count == 4:
break
print ('End of program')
Output
This will generate following output.
1 2 3 4 End of program
break statement is always used with if statement inside a loop and loop will be terminated whenever break statement is encountered.Python continue statement
Continue statement is used to skip the remaining statements in the body of that loop and continue the next iteration of the loop.
Unlike break statement, continue statement when encountered doesn’t terminate the loop, rather interrupts a particular iteration only.
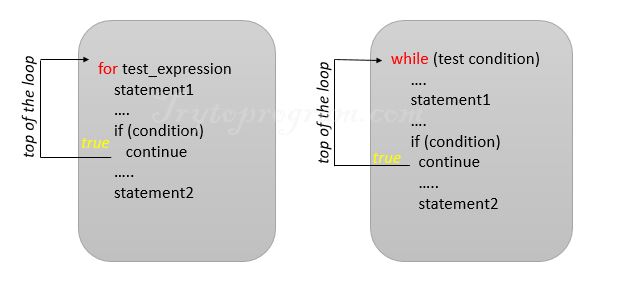
Syntax of Python continue statement
while (test_expression1):
statement(s)
if (test_expression2):
continue
|
for var in sequence:
statement(s)
if (test_expression2):
continue
|
The structure of Python break and continue statement is same except the keyword break and continue.
Flowchart of Python continue statement
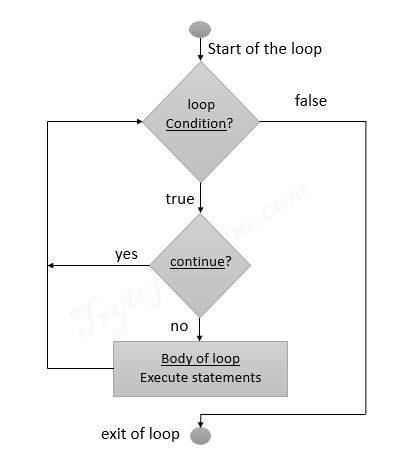
How continue statement works in python?
Example of Python continue statement in while loop
In the following example, while loop is set to print the first 8 items in the tuple starting from 8 to 1. But what actually happens is, when the count is equal to 4, it triggers if statement and the continue statement inside it is invoked making the program to skip the code below it. So, in the fourth iteration it was supposed to print 5, which is skipped.
#declaring a tuple
num = (1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8)
count = 8
while (count>0):
count = count-1
if count == 4:
continue
print (num[count])
print ('End of program')
Output
This script will generate following output.
8 7 6 4 3 2 1 End of program
Example of Python continue statement in for loop
Following example will print 'YOO' in the output console instead of 'YOLO' because when the iteration comes to letter 'L', the print statement will be skipped and the next iteration of for loop will continue.
for letter in 'YOLO':
if letter == 'L':
continue
print (letter)
Output
This will generate following output.
Y O O
So, this is all about Python break and continue statement. We hope you didn’t have a hard time understanding the concepts of break and continue statements.