Batch file Network Commands: NET
In this tutorial, you will learn in depth about batch file network commands: NET with examples.

Batch file NET commands are used to manage and troubleshoot any aspect of the network with lot more exciting features.
For those who are not familiar with command line and batch file, we will guide you through every aspect of net command.
Batch file: NET command
We can use NET commands for managing our network as well as troubleshooting locally and remotely in any network.
There are 21 sub-commands with its own switches.
Don’t panic we will explain each and every command.
Syntax of net command:
NET [ACCOUNTS | COMPUTER | CONFIG | CONTINUE | FILE | GROUP |
HELP | LOCALGROUP | PAUSE | SESSION | SHARE | START |
STATISTICS | STOP | TIME | USE | USER | VIEW ]
If you are new to this command, then NET HELP command explains different types of names and syntax of NET command as follow:

Now let’s take a look at one of the interesting NET subcommand i.e. USER
Batch file command: NET USER
NET USER command is used for viewing, creating, deleting and setting the password for an existing or newly created accounts in windows.
For this, we should run command line with administrative privileges.
Syntax of NET USER command:
C:\> NET USER
This command will display all the users in you local machine.
The NET command with USER or USERS will perform the same operation.
As seen in the above picture, there are five different users on my local machine i.e.
'Administrator', 'DefaultAccount', 'Guest', 'ICT' and WDAGUtilityAccount'
The Administrator and Guest are default accounts created when we install an operating system.
Administrator user has admin rights whereas Guest belongs to the same category with fewer privileges.
I created ICT account when installing windows.
Other accounts were created by the operating system for different purposes such as remote access, troubleshooting, and updates.
Adding the new user using a command line and Batch file.
So let’s have some fun using NET subcommand USER along with the '/add'.
C:\> NET USER "username" "password" /addwhere,
username = new username you want to add
password = password for the new username
Let’s run the command:
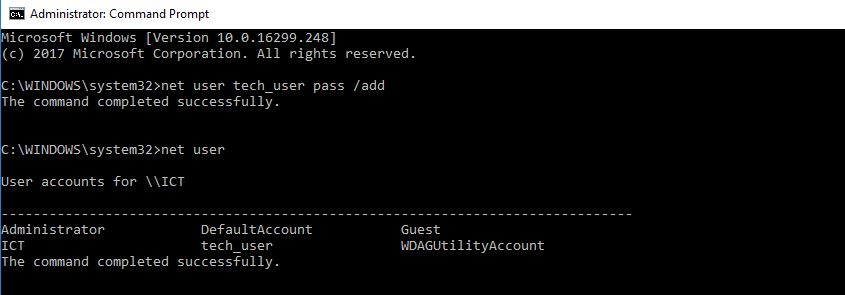
As we can see in the above picture, we have created a new account named tech_user with pass as a password.
This tech_user have normal privileges and restricted from installing new software and access to restricted folders.
This can be done using the batch file as follow:
@echo off net user tech_user pass /add
Write the above code in notepad and save it with .bat extension. Run the saved file using administrator rights the new user will be created in your computer.
Changing password of the newly created account using command line
C:\> NET USER tech_user *
Type a password for the user:
Retype the password to confirm:Type new password, confirm it and see the result.

The above code will change the password.
Changing password of user account using batch file
@echo off
net user tech_user *
If you run this file, it will ask for new password.
Deleting user account using command line
We can also delete the user account using NET USER command with ‘/delete’.
Syntax
C:\> NET USER user_name /deleteLet’s run this syntax in command line

Now we can see that tech_user account has been successfully removed from the computer.
Batch file syntax for deleting user account
@echo off
net user tech_user /deleteWhat if you want to see detailed information about a specific user?
For this, we have following syntax
C:\> NET USER user_nameThis command will display account information, password last set, password expiry, whether the user has right to change the password and other information.

Assigning administrator rights to the user account
As said earlier, by default newly created account doesn’t have administrator privileges.
However, we can assign administrator rights to the accounts using the command line.
For this, we have to use localgroup subcommand.
C:\> net localgroup administrators tech_user /add
Now, I have assigned tech_user account to the administrator group which means it now has administrator privileges.
Again for deleting the user, we have to use the above mentioned /delete command.
Starting and stopping specific services supported by computer using the command line
There are various services running on the computer which can be viewed from services.msc.
Let’s try to start and then stop print spooler service using the command line.
Syntax
C:\> net start service_name
C:\> net stop service_namewhere,
service_name = specific service name
Starting print spooler service

Stopping print spooler service
