In this article, you will learn about C math library function asin() that returns arc sine value, with explanation and example.
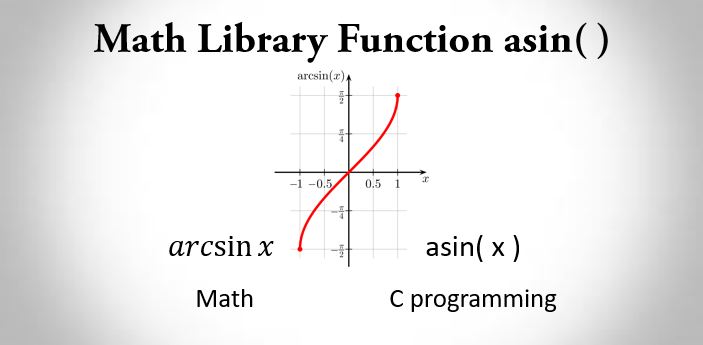
asin() is the standard C math library function that is defined in math library math.h.
#include<math.h>Function prototype of C math library function asin()
double asin( double x );where,
x = floating point value between 1 and -1 (1 >= x >= -1).
Return Value of asin()
This function returns the arc sine (inverse sine) in radians of x that ranges in the interval [ -pi / 2, +pi / 2 ].
Note: asin() takes argument between 1 and -1 because the value of sine is in the range of 1 and -1.
Example: Program to demonstrate the use of C math library function asin()
/*Use of math library function asin*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
#define PI 3.1415926
int main()
{
double x, y;
x = 0.5;
y = -0.5;
//calculation arc sine in radians
printf("asin(%.2lf) = %.2lf (radians)\n\n", x, asin( x ));
//calculation arc sine in degrees
printf("asin(%.2lf) = %.2lf (degree)\n\n", x, asin( x ) * 180 / PI );
//calculation arc sine in radians
printf("asin(%.2lf) = %.2lf (radians)\n\n", y, asin( y ));
//calculation arc sine in degrees
printf("asin(%.2lf) = %.2lf (degree)\n", y, asin( y ) * 180 / PI );
return 0;
}
Output
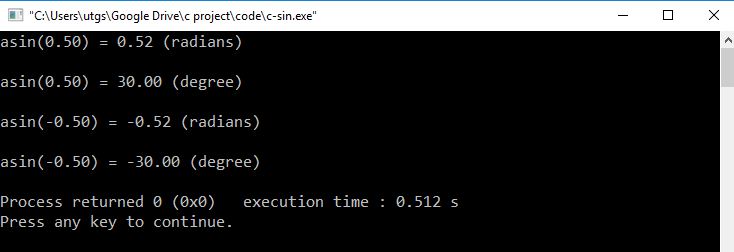
Explanation
In the above program, we have calculated the arc sine of x and y in radian and degree.
We have defined macro PI for representing the value of pi.