In this tutorial, you will learn in-depth about C string library function memchr( ) with explanation and explicit example.

memchr( ) is the built in standard library function that is defined in the string library string.h. Therefore, we should include string header library before using it.
#include<string.h>Function prototype of C string library function memchr( )
void *memchr( const void *str, int ch, size_t n );where,
str = Pointer to the object or block of the memory that needs to be scanned
ch = value that needs to be passed that is represented as unsigned char
n = Size of content in bytes to be scanned
This function searches for the first occurrence of a character ch in the n bytes of characters in the block of memory pointed by str.
It returns a pointer to the matching byte if the searched byte was found, otherwise, a NULL pointer is returned.
Let’s get a clear idea from the following example:
[adsense1]
C program to demonstrate the use of string library function memchr( )
/*Use of string library function memchr*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int main()
{
//initializing character pointer
const char *str = "Learn C from trytoprogram.com";
const char ch = 't';
//displaying str
printf("str = %s\n\n", str);
printf("Remaining string after '%c' : %s\n", ch, (char *) memchr( str, ch, strlen(str)));
return 0;
}//end
Output
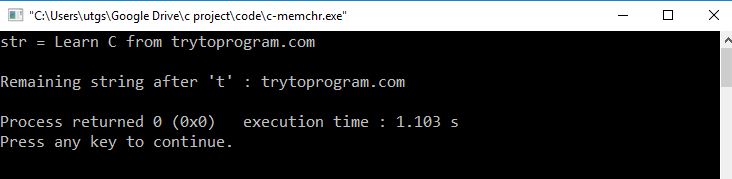
Explanation
In the above program, we have searched for 't' in the block of memory pointed by str.
strlen( ) is used to determine the length of str.
It locates the first occurrence of ch and displays the remaining string as shown in the output.