In this article, you will learn about C string library function memcpy( ) that is related to memory with step by step explanation and example.

Since memcpy( ) is the standard library function defined in string.h header file, we should include string library before using it.
#include<string.h>Function prototype of C string library function memcpy( )
void *memcpy( void *str1, const void *str2, size_t n );where,
str1 = Pointer to the destination array or object where content will be copied
str2 = Pointer to the source array or object from where content will be copied
n = size of content to be copied in bytes
This C string library function memcpy( ) copies n characters from the block of memory pointed by str1 to str2.
It returns a pointer to the block of memory or object where contents are copied.
Note: The pointers are declared as void * so that they can be used for any data type.
[adsense1]
This function does not check for terminating null character ‘\0’.
If you want to copy the characters in a same part of memory then we should use another string library function memmove( ) because the result of memcpy( ) is undefined in such cases.
C program to demonstrate the use of string library function memcpy( )
/*Use of string library function memcpy*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int main()
{
//declaring and initializing character array
char str1[ 50 ];
char str2[ ] = "Learn C from trytoprogram.com";
//displaying str1 and str2
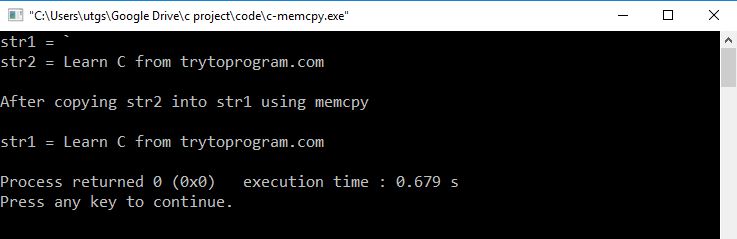
printf("str1 = %s\n", str1);
printf("str2 = %s\n", str2);
memcpy(str1, str2, strlen(str2) + 1);
printf("\nAfter copying str2 into str1 using memcpy\n"
"\nstr1 = %s\n", str1);
return 0;
} //end
Output
Explanation
In the above program, we have used two standard string function memcpy( ) and strlen( ).
strlen( ) is used to determine the length of str2.