Python bool() Function
The Python bool() function converts a value into a boolean value i.e either True or False using the standard truth testing procedure.
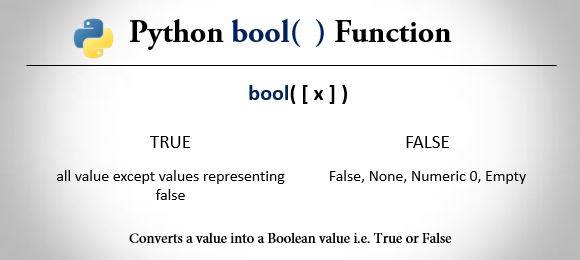
Python bool() Syntax
bool([x])Here x is the parameter passed. If no any parameter is passed, then the bool() function simply returns False.
So bool() returns False if x is omitted or False, else it returns True.
Note: The bool class cannot be subclassed further and its only instances are True and False.
How bool() works?
Well, how bool() works and how values are converted into boolean value depends on their truth values.
In general, following values are considered False in Python.
- False
- None
- Numeric 0
- Empty containers or sequences i.e. empty list, tuple, dictionary, strings etc.
All values except above-mentioned ones are considered True in Python.
Python bool() Example
>>> bool(0) #int
False
>>> bool(0.0) #float
False
>>> bool(0j) #complex
False
>>> bool('')
False
>>> bool([])
False
>>> bool(())
False
>>> bool({})
False
>>> bool(None)
False
>>> bool(1)
True
>>> bool(2.5)
True
>>> bool([0])
True
>>> bool((None,))
True
>>> bool({None: False})
True